Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Comparison of soluble and insoluble organic matter in analogues of Titan’s aerosols
Comparison of soluble and insoluble organic matter in analogues of Titan’s aerosols
Date de publication: 7 mai 2018
J. Maillard, N. Carrasco, I. Schmitz-Afonso, T. Gautier, C. Afonso
Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 495 185-191 (2018). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Rouen.
Abstract
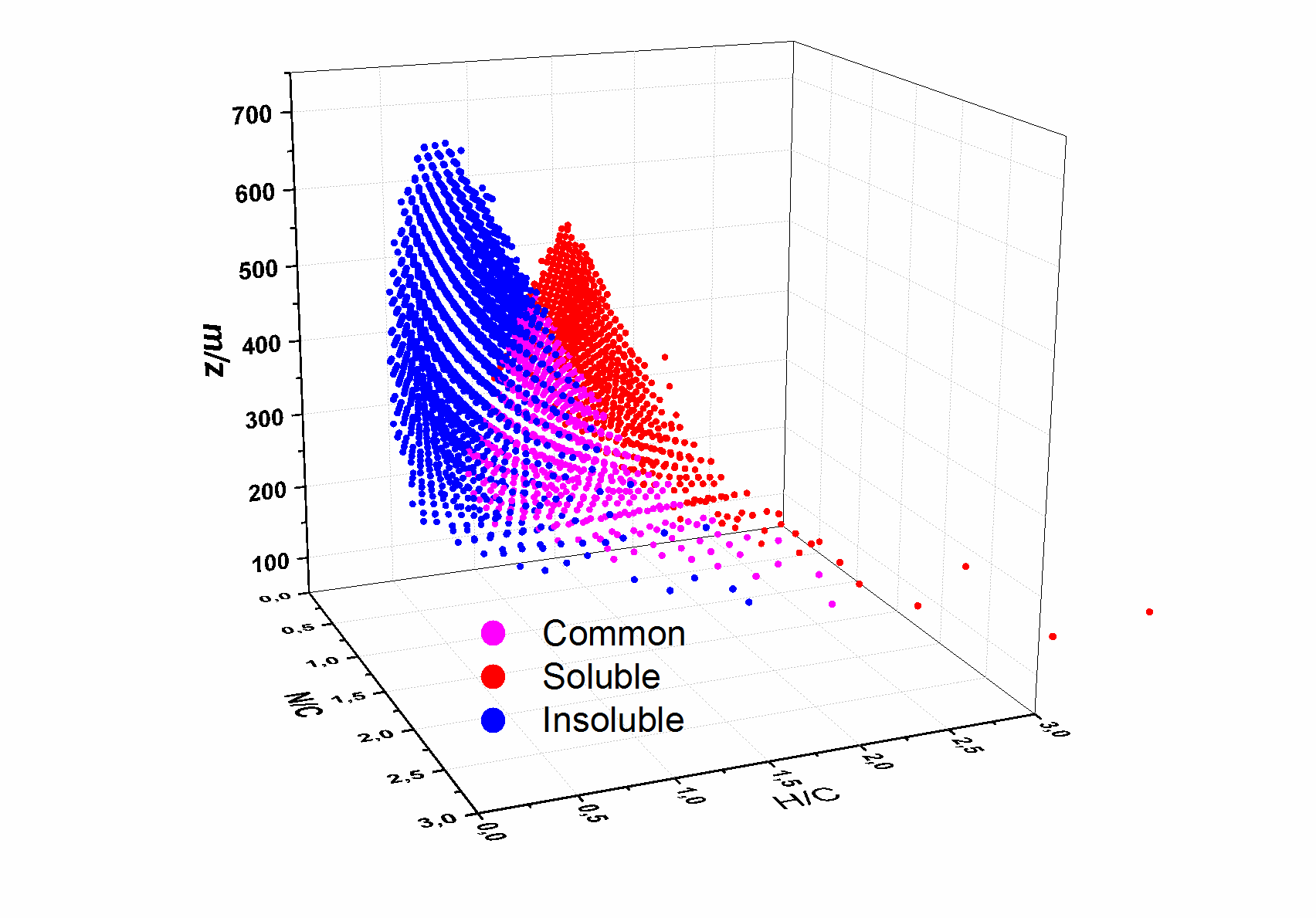
Titan, the biggest moon of Saturn, has a thick atmosphere which presents similarities with the one thought to be on Earth at its beginning. The study of Titan’s photochemical haze is thus a precious tool in gaining knowledge of the primitive atmosphere of Earth. The chemistry occurring in Titan’s atmosphere and the exact processes at act in the formation of the hazes remain largely unknown. The production of analogs samples on Earth has proved to be a useful tool to improve our knowledge of the aerosols formation on Titan. Such solid organic analogs samples, named tholins, were produced with the PAMPRE experiment (French acronym for Aerosols Microgravity Production by Reactive Plasma). PAMPRE tholins were found to be mostly insoluble, with only one-third of the bulk sample that can be dissolved in methanol. This partial solubility limited the previous studies in mass spectrometry, which were done only on the soluble fraction. The goal of the present study is to compare the two fractions of PAMPRE’s tholins (insoluble and soluble) using a ultra-high resolution Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTICR) equipped with a laser desorption/ionization source. Using modified Van Krevelen diagrams, we compare the global distribution of the molecules within the samples according to their Hydrogen/Carbon ratio and Nitrogen/Carbon ratio. Major differences are observed in the molecular composition of the soluble and the insoluble fraction. The soluble fraction of tholins was previously identified as a set of polymers of average formula (C2H3N)n. In this work we observe that the insoluble fraction of tholins is comprised of a significantly different set of polymers with an average composition of (C4H3N2)n.








