Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Tyrosine side-chain catalyzed proton transfer in the YG a2 ion revealed by theory and IR spectroscopy in the ‘fingerprint’ and XH (X=C, N, O) stretching regions
Tyrosine side-chain catalyzed proton transfer in the YG a2 ion revealed by theory and IR spectroscopy in the ‘fingerprint’ and XH (X=C, N, O) stretching regions
Date de publication: 15 avril 2012
B. J. Bythell, O. Hernandez, V. Steinmetz, B. Paizs, P. Maitre
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 316-318 227-234 (2012). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Université Paris-Sud.
Abstract
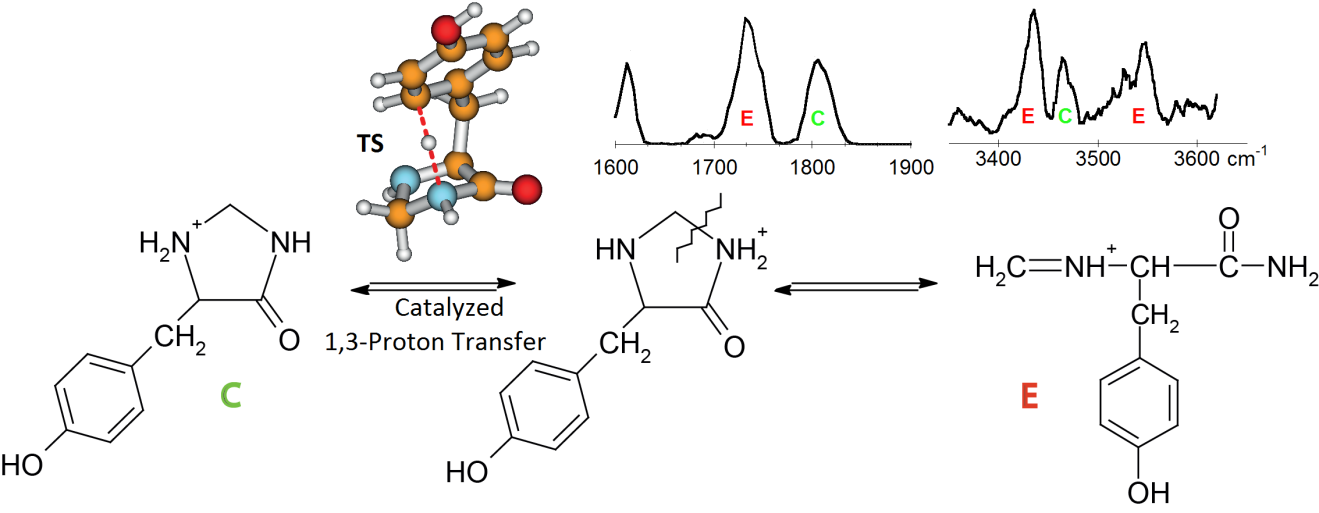
IRMPD spectroscopy in the ‘fingerprint’ and X-H (X=C, N, O) stretching regions was used to probe the structures of the YG a2 ions generated from protonated YGGFL and doubly protonated YGGFLR. Our experiments indicate a mixture of cyclic and rearranged ‘imine-amide’ structures. The cyclic isomer is generated from the initially formed protonated imine terminated linear structure by head-to-tail cyclization. Proton transfer between the secondary amine of the ring and the amide nitrogen followed by ring opening leads to the rearranged ‘imine-amide’ isomer. Quantum chemical calculations demonstrate that this proton transfer is catalyzed by the tyrosine side chain ring for the YG a2 ion. Isomer specific IRMPD bands observed in the two spectral regions clearly show the presence of the cyclic and rearranged ‘imine-amide’ isomers, the latter being characterized by an IR signature at 3545 cm-1 associated with the C-terminal amide NH2 asymmetric stretch.








