Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Comparison of collision-induced dissociation and electron-induced dissociation of singly charged mononucleotides
Comparison of collision-induced dissociation and electron-induced dissociation of singly charged mononucleotides
Date de publication: 15 avril 2012
V.H. Nguyen, C. Afonso, J.-C. Tabet
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 140 316 (2012). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Université Pierre et Marie Curie.
Abstract
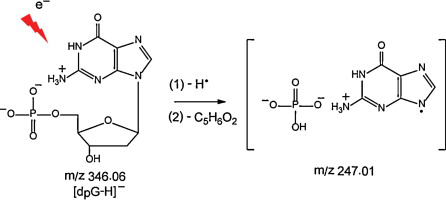
The dissociation of singlychargedmononucleotides by electroninduceddissociation (EID) and sustained off resonance irradiation/collisioninduceddissociation (SORI-CID) was investigated. The experiments have been carried out on deprotonated mononucleotides monomers. In general the same product ions are observed in the EID and SORI-CID spectra but some additional product ions have been obtained with EID. It was shown by MS3 experiments that all these additional product ions have been produced through consecutive dissociations of the [M−2H]− radical anion. In addition, H/D exchange and sequential MS3 experiments demonstrated that the m/z 247 fragment ion produced in EID of deprotonated 2-deoxyguanosine 5-monophosphate corresponds to the association of the phosphate group and the nucleobase. They were most likely linked by a non-covalent bond that was initially present in the precursor ion.








