Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Calmodulin association with the synthetic ERα17p peptide investigated by mass spectrometry
Calmodulin association with the synthetic ERα17p peptide investigated by mass spectrometry
Date de publication: 24 juin 2011
S. Bourgoin-Voillard, F. Fournier, C. Afonso, Y. Jacquot, G. Leclercq, J.-C. Tabet
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 305 87 (2011). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Université Pierre et Marie Curie.
Abstract
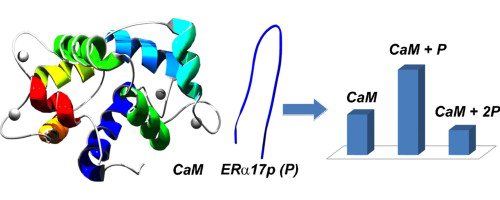
Implication of calmodulin (CaM) in breast cancer development has been proposed, justifying the interest for ER/calmodulin interaction. The association of the syntheticpeptide ERα17p (H–PLMIKRSKKNSLALSLT–OH), which corresponds to the known ER interaction site of CaM, was investigated. Under physiologically conditions, 1:1 complex formation was observed using an ESI-ITMS instrument. This equimolar complex with CaM was only formed in presence of calcium. The binding of ERα17p to CaM is probably due to presence of four basic residues (K299RSKK303) in its sequence. Its relative binding affinity in solution by ESI-MS was evaluated by performing competitive binding experiments with other peptides more (ERα17pKR : KRSKR) or less basic (ERα17pAA : KRSAA) than ERα17p as well as Melittin (Mel), selected as a reference peptide since it is known to form a high-affinity complex with CaM. Relative affinities of these peptides for CaM were classified in the following decreasing order :
Mel > ERα17pKR ∼ ERα17p ≫ ERα17pAA. Interestingly, another ion series showing two peptides for one protein was detected. The specificity of this complex not often reported for Melittin is discussed.








